The COVID-19 pandemic has brought significant disruptions to global supply chains, highlighting their vulnerabilities and prompting a reevaluation of their resilience. As the world moves toward recovery, assessing the lessons learned from this crisis and exploring the changes and innovations necessary to build more robust and agile global supply chains is crucial. Here are some challenges global supply chains faced during the pandemic and the potential strategies and trends that will shape their future in a post-pandemic world.

Dawn Downes/ CNN | Companies are still facing the long-lasting effects of COVID-19 on the supply chain
Supply Chain Disruptions
The pandemic exposed vulnerabilities in global supply chains, particularly in sectors heavily reliant on international sourcing and just-in-time inventory management. Lockdowns, travel restrictions, and factory closures disrupted the flow of goods, leading to shortages of essential products, including medical supplies, personal protective equipment (PPE), and electronic components. These disruptions highlighted the need for diversified sourcing, increased stockpiling of critical items, and enhanced visibility across supply chains.
Reshoring and Nearshoring
One major trend that emerged during the pandemic was the reconsideration of offshoring strategies. Companies realize the risks of relying heavily on a single country or region for their supply chain operations. Reshoring, which involves bringing production back to the domestic market, and nearshoring, which involves locating production closer to the end market, gained traction as companies sought to reduce supply chain risks and ensure greater control and flexibility. This trend is expected to continue in a post-pandemic world as companies aim to balance cost efficiency and risk management.
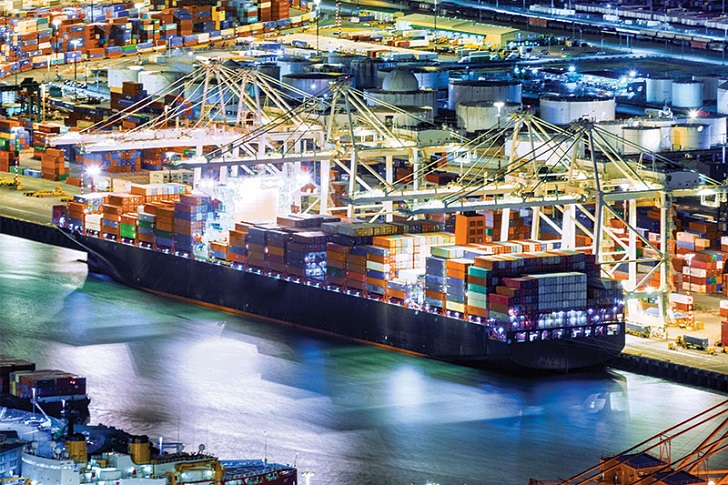

Jeff Berman/ Twitter | Major logistics disruptions have created a ripple effect on the global supply chain
Digital Transformation and Automation
The pandemic accelerated the adoption of digital technologies and automation in supply chain operations. Remote work, virtual collaboration, and digital communication tools are essential to maintaining business continuity. Supply chain visibility platforms, predictive analytics, and artificial intelligence (AI) gained prominence as companies sought to improve demand forecasting, optimize inventory management, and enhance supply chain resilience. Investments in robotics and automation technologies also increased as companies looked to reduce reliance on manual labor and mitigate the impact of future disruptions.
Sustainability and ESG Considerations
The pandemic raised awareness of the importance of environmental, social, and governance (ESG) factors in global supply chains. Consumers and investors alike have become more conscious of sustainability issues, demanding greater company transparency and accountability. In response, stakeholders focus on reducing carbon emissions, minimizing waste, ensuring fair labor practices, and promoting supply chain traceability. Integrating ESG considerations into supply chain strategies will likely gain momentum in the post-pandemic era.

Studio DB/ Pexels | The pandemic served as a wake-up call for many companies
Agility and Flexibility
The ability to quickly adapt to changing market conditions and disruptions is crucial for supply chains in a post-pandemic world. Companies are reevaluating their supply chain strategies to enhance agility and flexibility. This includes developing alternative sourcing options, building robust risk management frameworks, and implementing dynamic demand forecasting models. Collaboration and information sharing among supply chain partners are vital for real-time visibility and responsiveness.
Government Policies and Trade Relations
The pandemic underscored the interdependence of global economies and the impact of government policies on supply chains. Trade restrictions, export bans, and geopolitical tensions disrupted the flow of goods and highlighted the need for collaboration and open dialogue among nations. Governments are expected to reassess their trade policies, diversify supply chain sources, and explore regional partnerships to reduce vulnerability to future disruptions. Enhanced cooperation and coordination between governments, industry stakeholders, and international organizations will be crucial for the stability and resilience of global supply chains.
show more